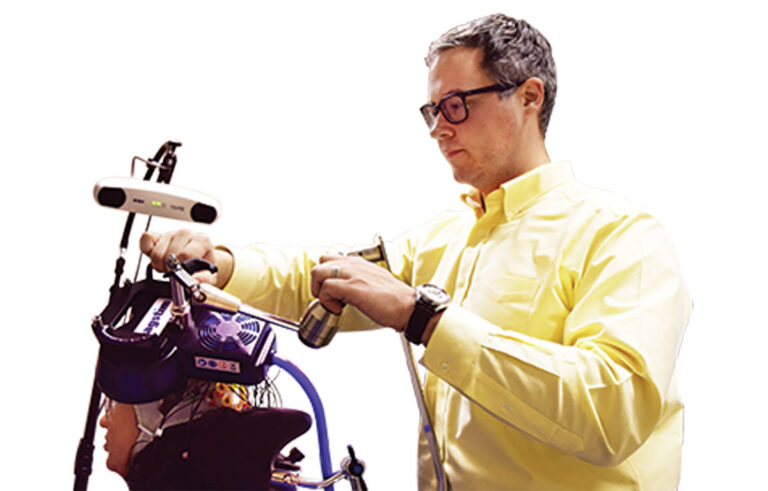
Despite growing interest in brain stimulation, researchers know little about the public’s ethical attitudes toward the use of the technique. That motivated John Medaglia, a professor of psychology, and his colleagues to ask over 800 individuals if they were more willing to use brain stimulation on others than on themselves, and if they were more willing to use it with the goal of repairing, rather than enhancing, cognitive functions. “Sometimes people will report that they’re willing to use brain stimulation in less moral ways when it suits themselves,” Medaglia says. “However, it’s encouraging to know that people are generally looking out for those who might be struggling the most.”
Symptoms of Sepsis
MEDICINE
Drexel researchers have identified the specific symptoms that put patients at the greatest risk of dying from sepsis — and they’re not what many clinicians might think. A new study shows that impaired kidney function is one of the leading predictors of sepsis patient mortality. Conversely, the researchers found that the more well-known symptoms of sepsis, such as low blood pressure, were linked to lower mortality rates in the population they studied. “Symptoms related to these systems need to be raising a red flag for doctors,” says study co-principal investigator Ryan Arnold, an emergency medicine doctor and faculty member at Drexel College of Medicine.
Health for all
PUBLIC HEALTH

Though Medicaid expansion has helped to improve insurance coverage for immigrant populations in the United States, uninsured rates still remain high for those in the United States who are not yet citizens, according to a new study by researchers at Drexel and the University of Nebraska Medical Center. The researchers found that the percentage of uninsured noncitizens decreased after the Affordable Care Act went into effect, from 70 percent in 2010 to 54 percent in 2015. However, when compared to other populations, uninsured rates for noncitizens remained high.
Joint Pain
BIOMED
Drexel’s Lin Han, an associate professor in the School of Biomedical Engineering, Science and Health Systems, has received a CAREER award from the National Science Foundation to study fibrous tissues at the nanoscale, advancing the treatment and understanding of cartilage diseases such as osteoarthritis. Funding from the award will allow Han’s lab to generate new knowledge about the biomechanics of the pericellular matrix — a thin coat that surrounds fibrous tissue cells. Recent studies have suggested that this “coat” could play a pivotal role in regulating fibrocartilage, which can be found, for example, in the knee joint meniscus. Han says this research will advance research into problems like incurable, chronic knee pain, which afflicts millions every year.
Shower Germs
ENGINEERING
Researchers from Arizona State and Drexel have taken a closer look at how the spray from showers, sinks and toilets can expose us to bacteria responsible for waterborne disease. The study focuses specifically on Legionella pneumophila, the bacteria that causes pneumonia-like Legionnaire’s disease. “We found that shower risks were highest, likely due to the amount of time a person would be exposed to the water spray,” says paper coauthor Charles Haas, LD Betz Professor of Environmental Engineering in the College of Engineering.


